Network Packet-Level
Protocol Analysis
Protocol Analysis
Packet Capture and Packet-Level Protocol Analysis Professional ServicesAlthough on-site services packet capture services that were offered through Connect802 Corporation prior to 2020 are no longer available you can still count on Maui Communications Networks as a resource to help you with Wireshark-compatible packet-level trace file analysis. Contact us for complete details.
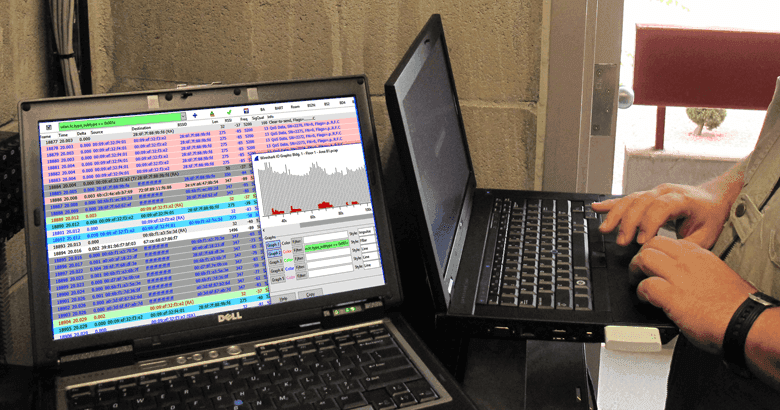
What is "Packet-Level Analysis" and why is it important?
"Packet-Level Analysis" is the process by which individual conversations between devices are captured using a Protocol Analyzer and then the captured packets are decoded so they can be examined and assessed for correct operation. Software tools like Wireshark, AirMagnet Spectrum XT, and OmniPeek are common examples of protocol analyzer software packages and these are used by the Connect802 protocol analysis team to provide packet-level analysis consulting services.
What is the process of performing analysis of 802.11, TCP/IP, and other protocols using a protocol analyzer?
User data and application software information is transferred across a wired Ethernet or wireless 802.11 WiFi network in collections of data bytes called "packets". Each packet contains information identifying the devices, programs, and operating system elements that are involved in the exchange of data. Internal configuration information, software requests, and their replies are part of the packet exchange. When conversations are analyzed at the packet level the specific overall operation and detailed internal behavior of the communicating devices is exposed. A trained, experienced protocol analysis engineer can examine the packet-level captured data and draw conclusions and develop meaningful insight regarding problem issues that are not necessarily related to 802.11 RF signals, noise, or interference.
What types of problems can be identified during packet-level trace file protocol analysis?
Because the internal behavior and state of the system and application software is revealed by the packet-level behavior, protocol analysis can disclose a variety of possible problem sources or inefficiencies. These are often highly technical in nature and the Connect802 protocol analysis engineering team has extensive experience understanding and interpreting packet-level behavior. In fact, members of our team have provided protocol analysis training courses, seminars, and consulting services to companies across the United States and in Europe going back to 1988! (That was 2 years after the introduction of the first commercial protocol analyzer, the Network General Sniffer Analyzer). Problems that are manifested at the protocol level include:
- Default Gateway IP address assignment by DHCP
- Incorrect DNS server specification
- DHCP lease time misconfiguratoin
- TCP stack overflow and buffer memory deficit
- RADIUS 802.1x credential failure
- VLAN misconfiguration
- QoS priority issues
- 802.11 CTS/RTS implementation errors
- IP address conflicts
- Frame or data payload size limitations
- Block-ack misconfiguration errors
- Unauthorized network access attempts
- Denial-of-Service attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle hacking attempts
- Wi-Fi Direct and wireless printer issues
When It Comes To Wireless Network Protocol Analysis - We Wrote The Book!
Literally; we wrote the book! Joe Bardwell, your engineering resource at Maui Communications Networks, wrote the 802.11 wireless network protocol analysis section of this Wiley network analysis book. "Troubleshooting Campus Networks", co-authored by Priscilla Oppenheimer and Joseph Bardwell, provides solid explanations of network and wireless protocols and how they are expected to behave when analyzed with a protocol analyzer tool. When you work with Maui Communications Networks you're working with experts that are recognized in the industry for their experience and excellence. Click the book cover image to search inside the text.
How Does A Protocol Analysis Engineer Isolate and Describe Network Problems at the Packet Level?
- Software tools like WireShark, AirMagnet SpectrumXT, OmniPeek, and others capture a trace file with copies of the 802.11 control, management, and data frames along with the TCP/IP and related packets being transmitted across a network. In the case of 802.11 protocol analysis the trace file can be captured directly from the air or may be acquired by utilizing packet capture features available in Ruckus Wireless, MIST Systems, and other commercial access point and controller systems.
- The protocol analyzer software knows how to decode the bytes and bits in captured packets and the protocol analyzer output presents the packet contents in plain text.
- Three views of the data are presented in a protocol analyzer user interface: Summary, Detail, and Hex.
- The Summary View shows, row-by-row, each captured packet
- The Detail View presents the fields and their contents inside one selected packet. (An example of a portion of the Detail View of a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) packet, as seen in the Wireshark Detail View, is shown below.)
- The Hex View lets the protocol analysis engineer study the bit and byte contents of the packet
- During packet-level analysis an assessment is made to confirm the correct and expected behavior concerning the sequence of events in the packet summary as well as the specific commands, responses, acknowledgements, and management/control behaviors in packet detail
Network protocol behavior is defined and documented by the IEEE and the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) as well as by manufacturer-specific implementation notes. The Connect802 protocol analysis engineering team has been using protocol analyzer tools and evaluating network behavior since 1988. Over the intervening 30+ years we've watched the evolution of computer communications and we know what to expect when we evaluate a wired Ethernet or a wireless 802.11 WLAN.

DHCP Protocol Analysis Packet Detail View Example
TCP/IP Protocol Analysis Technology Examples - Internet Request For Comment RFC-793
The expected and specified behavior of Internet Protocols (DHCP, DNS, IP, TCP, etc.) are defined in "Request For Comments" documents ("RFCs"). This name refers to the fact that when the Internet Protocols were being created it was a group effort and many stake holders presented their opinions. RFC-793 defines the behavior of Transmission Control Protocol, TCP. A brief section of the RFC is presented here, without elaboration, as an example of the expected protocol behavior that would be analyzed during a Connect802 TCP/IP packet-level analysis engagement. The Connect802 team knows how to interpret the decoded trace files captured from a network and compare the observed behavior to the expected behavior to provide verification or problem isolation and description.
_______________________________________________________________
A connection progresses through a series of states during its lifetime. The states are: LISTEN, SYN-SENT, SYN-RECEIVED, ESTABLISHED, FIN-WAIT-1, FIN-WAIT-2, CLOSE-WAIT, CLOSING, LAST-ACK, TIME-WAIT, and the fictional state CLOSED. CLOSED is fictional because it represents the state when there is no TCB, and therefore,no connection. Briefly the meanings of the states are:
- LISTEN - represents waiting for a connection request from any remote TCP and port.
- SYN-SENT - represents waiting for a matching connection request after having sent a connection request.
- SYN-RECEIVED - represents waiting for a confirming connection request acknowledgment after having both received and sent a connection request.
- ESTABLISHED - represents an open connection, data received can be delivered to the user. The normal state for the data transfer phase of the connection.
- FIN-WAIT-1 - represents waiting for a connection termination request from the remote TCP, or an acknowledgment of the connection termination request previously sent.
- FIN-WAIT-2 - represents waiting for a connection termination request from the remote TCP.
- CLOSE-WAIT - represents waiting for a connection termination request from the local user.
- CLOSING - represents waiting for a connection termination request acknowledgment from the remote TCP.
- LAST-ACK - represents waiting for an acknowledgment of the connection termination request previously sent to the remote TCP (which includes an acknowledgment of its connection termination request).
- TIME-WAIT - represents waiting for enough time to pass to be sure the remote TCP received the acknowledgment of its connection termination request.
- CLOSED - represents no connection state at all.
802.11 WiFi Network Protocol Analysis Technology Examples
In the realm of 802.11 WiFi there are three categories of MAC frames: Management, Control, and Data. Data frames carry, typically, internet protocols such as IP, TCP, DHCP, DNS, RADIUS, and so forth. Management and Control frames are used by the communicating device's firmware and device driver code to make 802.11 work. The expected behavior of 802.11 packets is defined by the IEEE in the "802.11 Standards". A Connect802 WLAN protocol analysis engineer will look at the various interactions at Layer 2, the MAC layer, to confirm proper interoperation between access points and client devices. Frames include the following:
- Authentication frame
- In 802.11, authentication is the process of an access point accepting the identity of a radio interface card. The process begins by the radio sending an authentication frame to the access point and then the access point sending an authentication frame indicating an acceptance or rejection.
- Deauthentication frame
- A deauthentication frame is sent by a station to another station when it wishes to terminate communications.
- Association request frame
- Association allows the AP to reserve resources for a particular wireless interface. A wireless station begins by sending an association request from to an AP. This frame contains the SSID that the station wants to associate with and information about the wireless interface card.
- Association response frame
- An access point sends an association response frame when it receives an association request frame from another station. This response frame contains if it accepts or rejects the association. The frame also contains information regarding the association. Such as the association ID and supported data rates.
- Disassociation frame
- A station sends a disassociation frame when it wishes to end the association. This allows the AP to free resources that it allocated to the station
- Reassociation request frame
- A station sends a reassociation frame when the signal strength of the currently associated AP is low and there is a higher strength signal from another AP. The station will send a reassociation request to the new AP.
- Reassociation response frame
- An AP sends an acceptance or rejection to the station sending the reassociation request. This frame also contains information about the AP.
- Request To Send frame
- A transmitting device sends an RTS frame to notify the rest of the wireless broadcast domain that it's about to transmit a packet which requires a specified amount of time in the air.
- Clear To Send frame
- An access point, after receiving an RTS frame, sends the CTS frame which is heard by all stations in the coverage cell and which informs them that the air is reserved for the specified period of time. This addresses situations where a coverage cell is very large or where channel overlap is present and is causing degradation.
Talk To The Experts At Connect802 When You Need On-Site Resources To Perform:
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting Office Building WiFi
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Apartment Complex s
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Hospitals
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Research Labs
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Hospitality
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Resorts
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Hotels
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Automotive Car Dealerships
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Marinas and Boat Yards
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Museums and Aquariums
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Schools and Universities
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Warehouses
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Military Bases
- Packet-Level Protocol Analysis for Troubleshooting WiFi in Outdoor Venues
- Protocol Analysis Using AirMagnet Spectrum XT
- Protocol Analysis Using WireShark
- Protocol Analysis Using OmniPeek
Perspective On Wireless Network Packet-Level Protocol Analysis and Protocol Analyzer Software Tools
At Connect802, our consulting and engineering services include packet-level analysis with a protocol analyzer. Packet-level protocol analysis is accomplished with a software protocol analyzer that runs, typically, on a notebook or similar computer. There is an aspect of hardware operation that must be addressed in order for a computer to capture packets from the air. Normally a wireless client device associated to a specific 802.11 access point to exchange data. When capturing wireless packets from the air an 802.11 WiFi adapter must behave differently.
"Promiscuous Mode" and Notebook Computer Operation
There is an operational mode called "promiscuous mode" that can be initiated for a WiFi adapter that tells it to ignore the destination address in acquired packets and simply pass them all up the protocol stack. Promiscuous mode requires, however, that the adapter be associated to an access point. It captures only those packets sent from that one access point. This was how wireless packet capture was initially performed in the early 2000's when the first wireless protocol analyzer software was developed.
For effective wireless network analysis, promiscuous mode does not provide a complete picture of network protocol operation. Because this mode would require the wireless card to be associated to an access point it would not capture all wireless frames in the environment. There are, in addition to 802.11 data frames (containing TCP/IP and other Ethernet-like traffic), 802.11-specific frames for WLAN management and control. By default, many wireless NIC drivers will not pass up 802.11 management and control frames and therefore would not be visible in the protocol analyzer. 802.11 wireless networks are half-duplex, and wireless NICs cannot listen (receive packets) while transmitting.
"RF Monitor Mode" for Packet Analyzer Software
Because of the problem of lost management and control traffic when using promiscuous mode, wireless analyzers place the NICs into a special mode called "RF monitor mode" In RF monitor mode, the wireless NIC card becomes a passive monitoring device without the ability to transmit. As a result, the packet capture NIC cannot be used as a normal WiFi adapter because normal wireless network operation is disabled. In RF monitor mode, wireless NICs listen to all 802.11-encoded signals on the channel on which they are currently monitoring. It's typical to find that a notebook computer running an adapter in RF monitor mode will have a second adapter that is associated to an access point for normal WiFi operation.
Finding the Best Location for Capturing Packets From the WLAN
Imagine a misconfigured client device transmitting faulty packets over the air. This device could be several hundred feet away from an access point. If an on-site wireless network engineer was capturing packets several hundred feet on the opposite side of the access point it's possible that only the packets transmitted by the AP would be received with sufficient signal strength and SNR to allow them to be properly acquired. Packets from the faulty client, on the opposite side of the AP, could end up being too weak to be captured. The same is true if a localized noise source was disrupting a client device's ability to received packets but the noise was not impacting the location where the protocol analyzer was capturing traffic.
Identifying the correct location to place a network analyzer is a key part of performing successful wireless network analysis. If the protocol analyzer is in a poor location the placement of the wireless analyzer can lead to incorrect conclusions regarding the wireless LAN environment. For example, the packet analyzer is capturing traffic too far away from the access point and the client of interest there might be lot of corrupted frames; however, the intended recipient may not be experiencing any frame corruption.
Protocol Analysis Consulting Support Services and the WireShark protocol analyzer
When you need help analyzing a trace file, the Connect802 TRAC service will provide you with a consulting resource to meet your project requirements. To capture a trace file all you need is the free and open-source WireShark software program. Wireshark is the world's foremost and widely-used network protocol analyzer. The WireShark protocol analyzer software is supported by a development-community-at-large and is not a commercial product. There are over 600 contributors who have provided packet dissector and driver code for WireShark. WireShark's primary sponsor is Riverbed Technology and they maintain the code base for the WireShark protocol analyzer software. There are two operating modes to be aware of with WireShark: local packet capture with a standard WiFi adapter and capture with RF Monitor Mode.
With WireShark running in your laptop computer, without any special WiFi adapter, you'll be able to capture only data packets sent from or to your computer. This means, in essence, you're only going to see TCP/IP-related traffic and you're not going to see any 802.11 control or management packets. This is because WireShark is capturing the packets that are passed up the protocol stack from the 802.11 driver - the TCP/IP, Ethernet-like packets. 802.11 control and management, and all data packets not addressed to your machine as the destination, are not passed up to the operating system by the 802.11 adapter driver.
When you're troubleshooting an Ethernet-like protocol (TCP/IP, DHCP, ARP, etc.) it may be sufficient to capture only Ethernet-like packets from a computer that is experiencing the problem. When troubleshooting problems like slow WiFi performance, inter-access point roaming, wireless authentication, CTS/RTS behavior, or other 802.11-related behavior then you'll need to capture with an adapter that supports RF Monitor Mode. Riverbed, the WireShark sponsoring company, developed the AirPcap adapter for RF Monitor Mode but this adapter was limited to 802.11b/g/n operation. WireShark remains the premiere packet analysis and decoding tool however it does have some hardware-related limitations regarding 802.11 WLAN packet capture over-the-air.



